Running and Scaling Tests
Scaling Test Executions
Scaling test executions involves leveraging your CI/CD infrastructure, your own resources, or a combination of both. Key aspects include:
Infrastructure Considerations
-
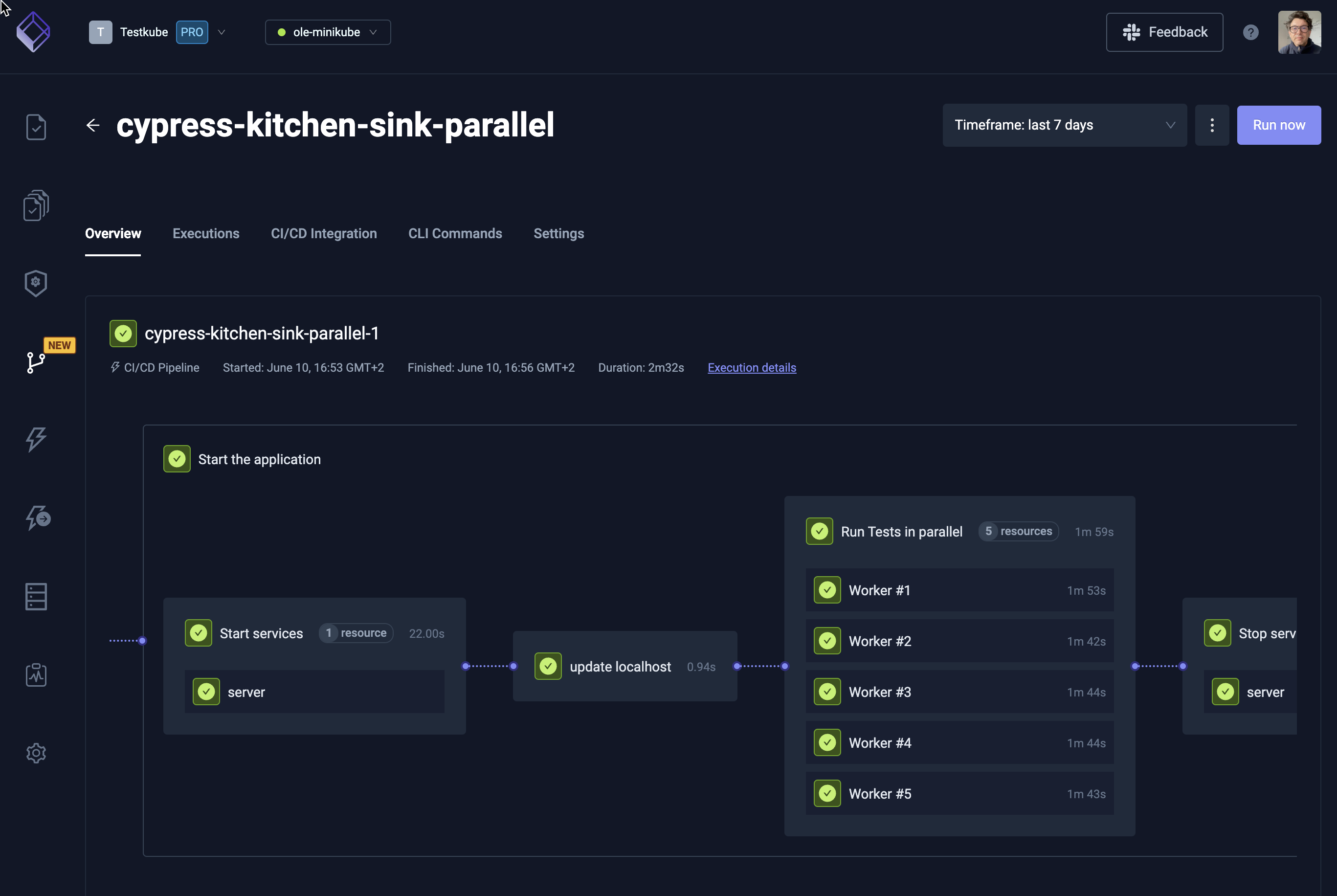
Parallel Execution:
Support for multiple tests running concurrently—especially useful when different teams or components are building at the same time. -
Scaling Individual Tests:
Ability to scale a single test:- Load Testing: Generate massive load.
- E2E Testing: Run tests across multiple browsers concurrently.
Avoiding Resource Collisions
- Ensure that concurrently running tests do not impact each other in terms of load or state on shared resources (unless intentionally desired).
Security Considerations
- Tests must have network/component access to the applications being tested.
- Running tests from outside the infrastructure may pose challenges, so ensure secure access paths are in place.
Running Tests with Testkube
Testkube leverages Kubernetes to execute your tests, offering several run-time benefits:
Kubernetes-Based Execution
- Automated Scaling:
The Kubernetes job scheduler manages scaling, enabling efficient resource allocation as long as Kubernetes itself has sufficient capacity.
Parallelization & Sharding
- Parallel Execution:
Use Test Workflows' built-in parallelization capabilities to run multiple tests simultaneously. - Sharding:
Scale the same test across multiple instances using sharding to generate massive load or test multiple permutations.
Optimizing Pod Usage
- Configure Test Workflow Pods for optimal performance using:
- Pod Affinity:
Control where your tests run. - Topology Spread Constraints:
Evenly distribute workloads across nodes.
- Pod Affinity:
Security Benefits
- Since tests run inside your clusters, external network access for testing tools is generally unnecessary.
- This setup enhances security and mirrors a production-like environment.
Further Reading
Learn more about resolving issues by reading our article on Troubleshooting Tests.