Test Workflows - Parallel Steps
This Workflows functionality is not available when running the Testkube Agent in Standalone Mode - Read More
It is often desirable to spread the execution of a test across multiple nodes, for example, to generate extended load with a performance testing tool, or to speed up execution of a test by breaking it into smaller parts (i.e. sharding).
Test Workflows have parallel steps, that allow you to distribute your test even dynamically, and among multiple cluster
nodes, which can further be combined with matrix and sharding to break
down execution into multiple parallel steps.
Syntax
To declare the parallel step, you need to specify the step with parallel clause - see Schema Reference.
Basic configuration
It allows to provide:
- similar properties as any other kind of step, i.e.
container,run,shellorsteps - general Test Workflow properties, like
job,podorcontent - matrix and sharding properties
parallelismto define maximum number of instances to run at oncedescriptionthat may provide human-readable information for each instance separately
Fetching logs
By default the logs for the parallel steps are saved. To disable them or make them conditional, you can use logs property.
It takes an expression condition, so you can dynamically choose whether it should be saved or not. Often you will use:
logs: neverto never store the logslogs: failedto store logs only if the step has failed
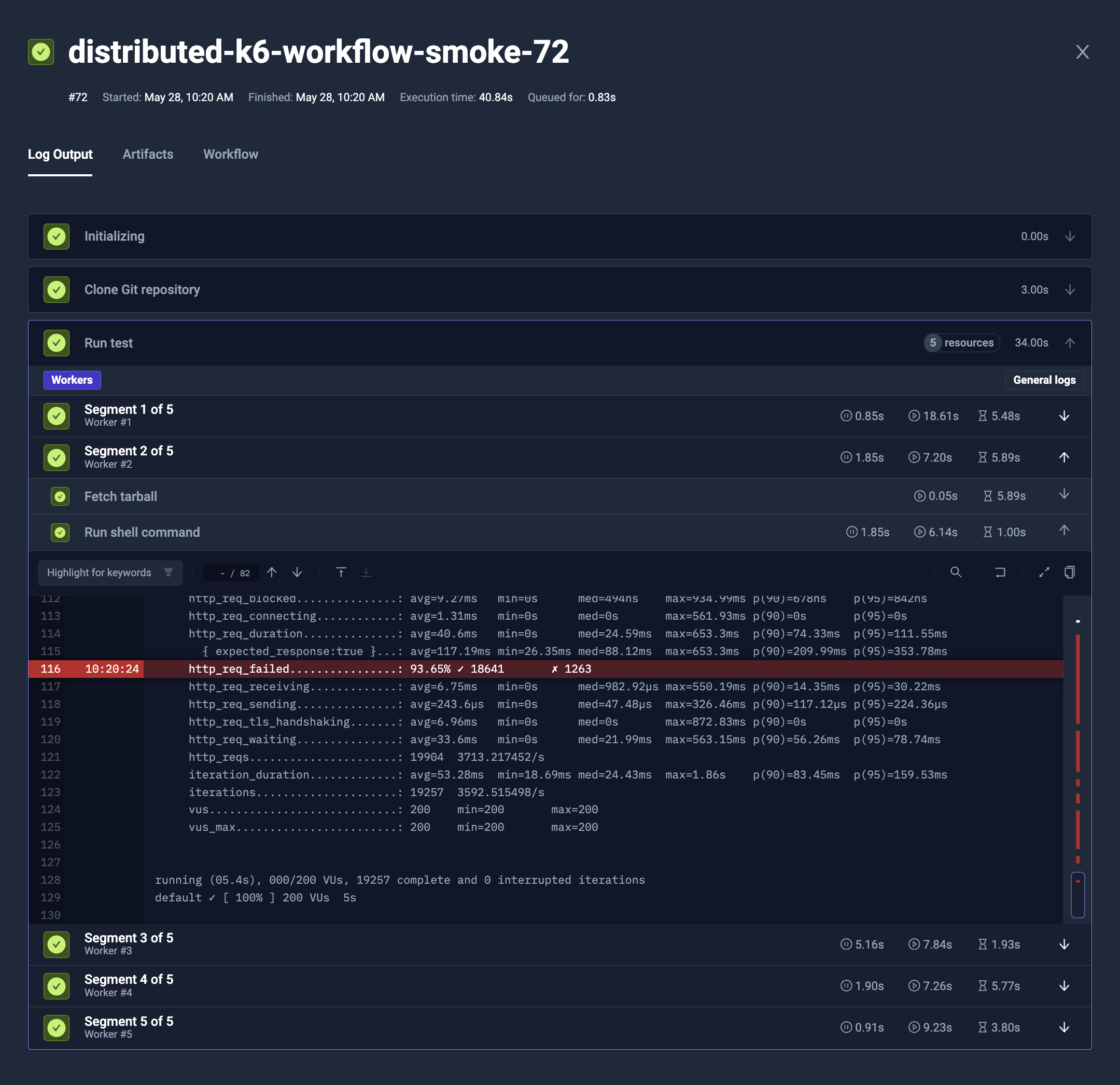
Pod and Job configuration
The parallel steps are started as a separate jobs/pods, so you can configure pod and job similarly to general Test Workflow.
Lifecycle
Similarly to regular steps, you can configure things like timeout (timeout: 30m), optional: true, or negative: true for expecting failure.
Matrix and sharding
The parallel steps are meant to support matrix and sharding, to run multiple replicas and/or distribute the load across multiple instances.
It is supported by regular matrix/sharding properties (matrix, shards, count and maxCount).
You can read more about it in the general Matrix and Sharding documentation.
Providing content
There are multiple ways to provide the files for the parallel steps.
As the parallel steps are started in separate pods, they don't share the file system with the Test Workflow execution.
Copying content inside
It is possible to copy the files from the original Test Workflow into the parallel steps. As an example, you may want to fetch the repository and install the dependencies on the original TestWorkflow, and then distribute it across the parallel steps.
To do so, you can use transfer property. It takes list of files to transfer:
{ from: "/data/repo/build" }will copy the/data/repo/builddirectory from execution's Pod into/data/repo/buildin the instance's Pod{ from: "/data/repo/build", to: "/out" }will copy the/data/repo/builddirectory from execution's Pod into/outin the instance's Pod{ from: "/data/repo/build", to: "/out", "files": ["**/*.json"] }will copy only JSON files from the/data/repo/builddirectory from execution's Pod into/outin the instance's Pod
Example
The example below will:
- Clone the Git repository (
content) - Install the Node.js dependencies (
steps[0].shell) - Run Playwright tests (
steps[1].parallel)- Specify 2 instances of that step (
steps[1].parallel.count) - Copy the
/data/repoalong with already installednode_modules(steps[1].parallel.transfer) - Run the Playwright test with customized
--shardparameter for each instance (1/2and2/2respectively, viasteps[1].parallel.shell)
- Specify 2 instances of that step (
- YAML
- Log Output
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: example-sharded-playwright-test
spec:
content:
git:
uri: https://github.com/kubeshop/testkube
paths:
- test/playwright/playwright-project
container:
image: mcr.microsoft.com/playwright:v1.32.3-focal
workingDir: /data/repo/test/playwright/playwright-project
steps:
- name: Install dependencies
shell: 'npm ci'
- name: Run tests
parallel:
count: 2
transfer:
- from: /data/repo
shell: 'npx playwright test --shard {{ index + 1 }}/{{ count }}'
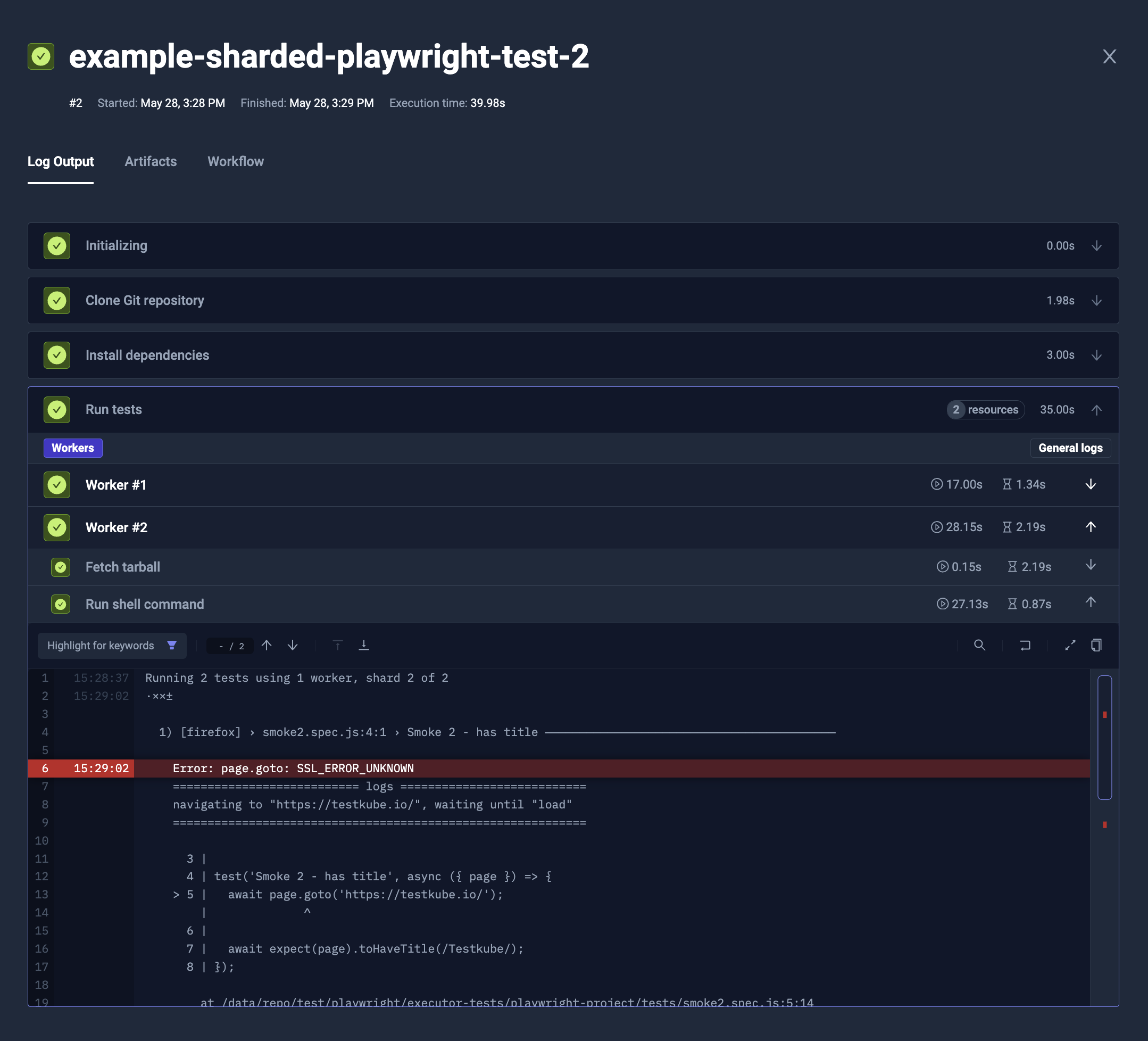
Static content or a Git repository
For distributed testing, it's better to avoid cloning repository in each step.
Instead, that could be run on sequential step, and then transferred to parallel steps with transfer.
This way you will spare the resources, as the computation and transferring over internet will happen only once.
Parallel steps allow to provide the content property similar to the one directly in the Test Workflow. As an example, you may clone the repository:
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: example-parallel-with-static-files
spec:
steps:
- parallel:
count: 2
content:
files:
- path: /k6.js
content: |
import http from 'k6/http';
export const options = {
thresholds: {
http_req_failed: ['rate<0.01'],
}
};
export default function () {
http.get('https://testkube.io/');
}
run:
image: grafana/k6:latest
shell: "k6 run /k6.js --iterations 100"
Synchronising the parallel steps execution
By default, each parallel step is executed as soon as it is possible. There is an option to override it though, so they won't start until all the instances are ready. The pods may start at different time, especially with node auto-provisioning.
It's especially useful for load testing, like K6, as you want to have the distributed load test executed at the same time.
To achieve that with parallel steps, simply add paused: true clause directly under the parallel, or to the specific step that it should stay at.
This way, the tests won't get started, until all steps have reached that point.
- YAML
- Log Output
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: example-parallel-with-static-files
spec:
steps:
- parallel:
count: 2
paused: true
content:
files:
- path: /k6.js
content: |
import http from 'k6/http';
export const options = {
thresholds: {
http_req_failed: ['rate<0.01'],
}
};
export default function () {
http.get('https://testkube.io/');
}
run:
image: grafana/k6:latest
shell: "k6 run /k6.js --iterations 100"
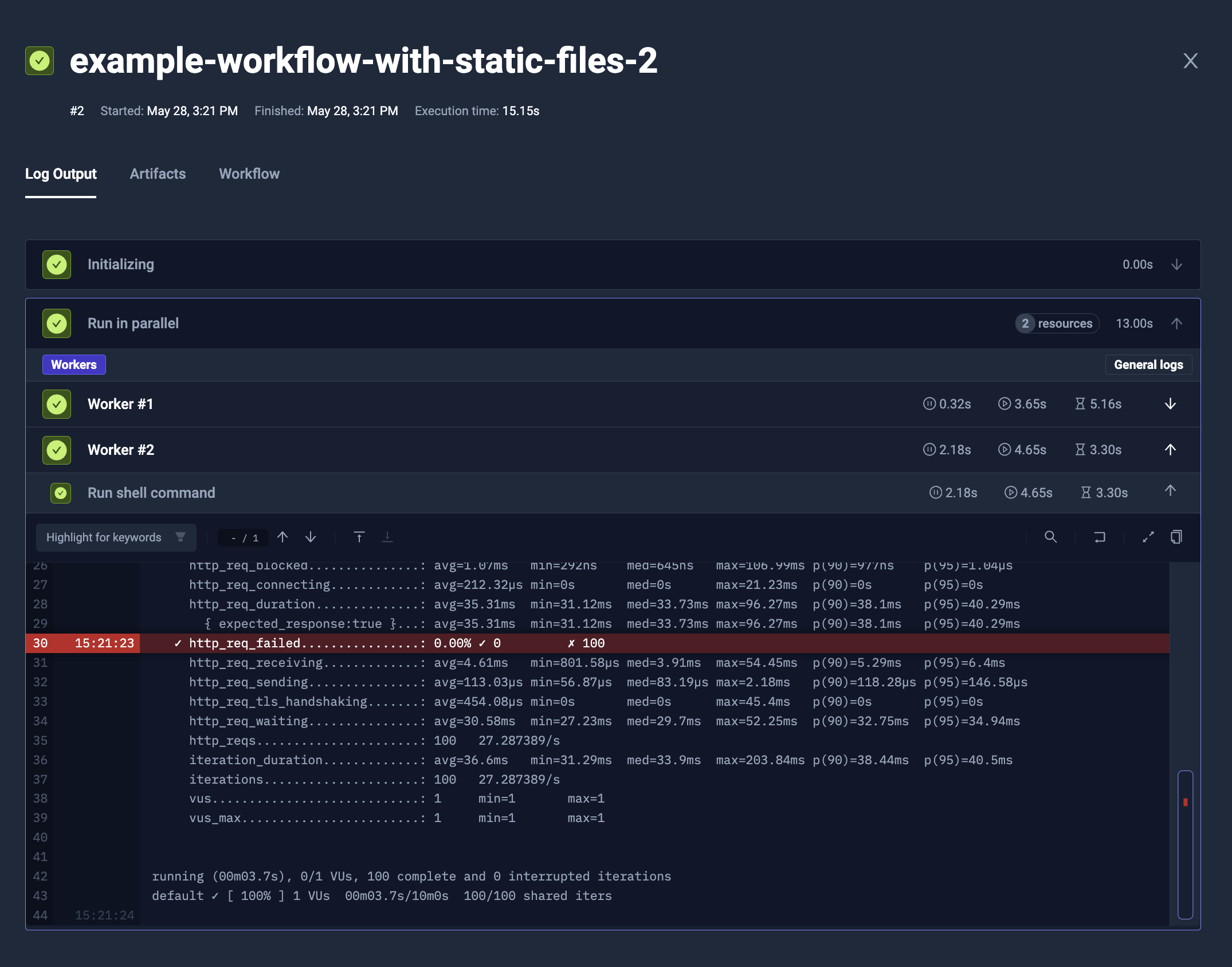
Reading files from parallel steps
In the opposite to copying the files into the parallel steps pod, you may want to read reports or other data from them too. There are 2 basic methods to achieve that.
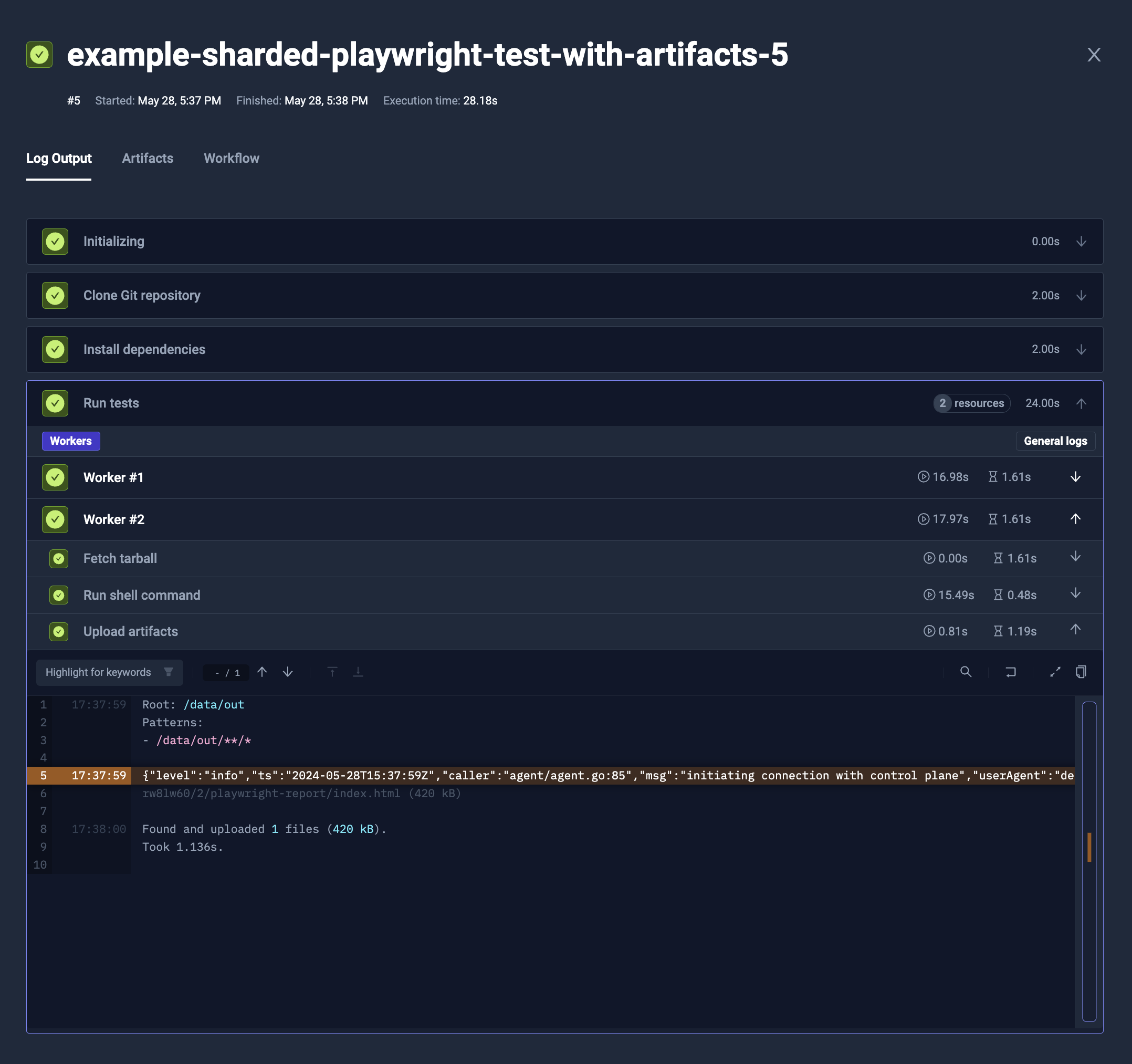
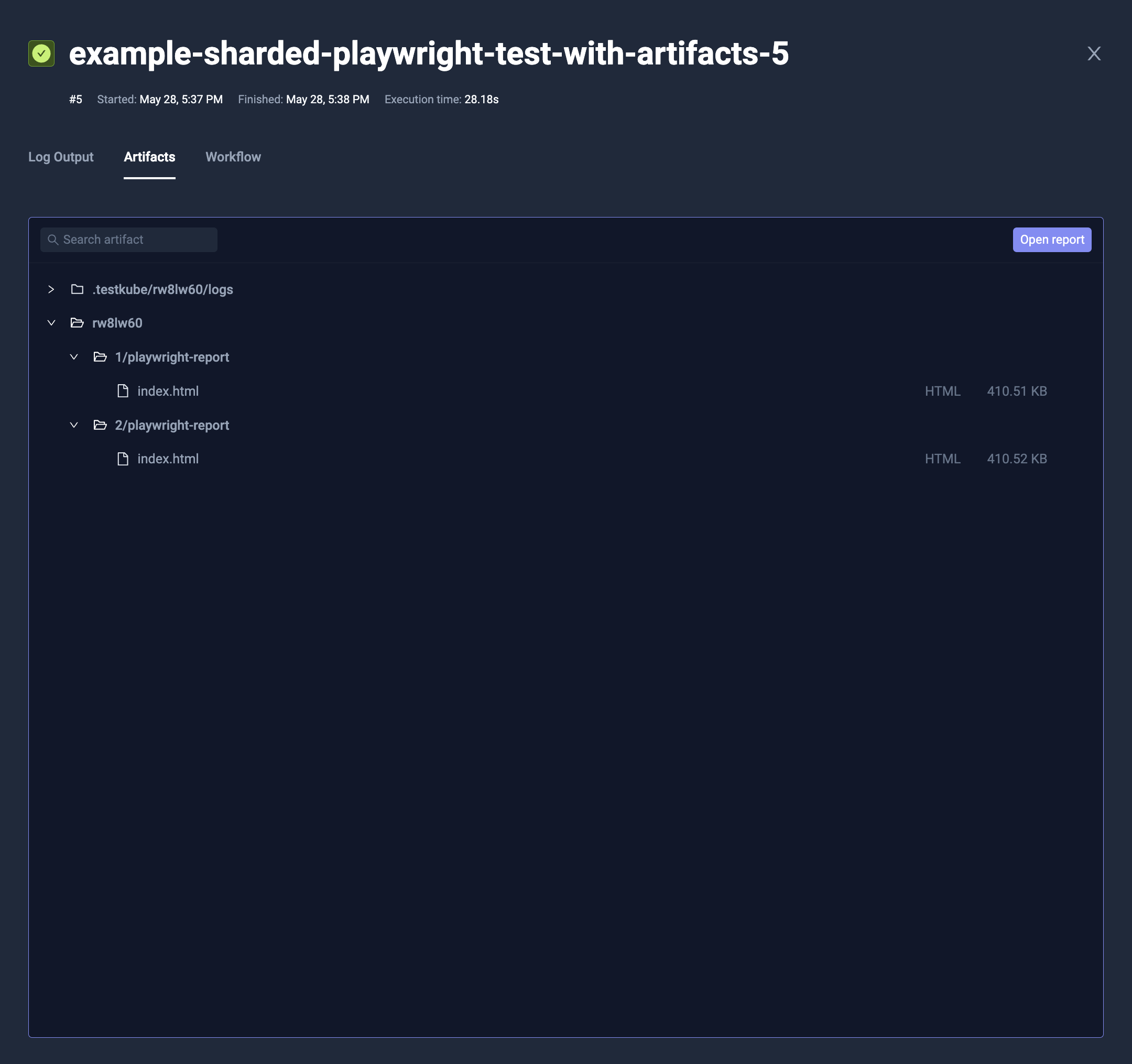
Artifacts
The parallel steps may expose data as artifacts, just the same way as sequential step. The artifacts from different steps will be isolated.
- YAML
- Log Output
- Artifacts
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: example-sharded-playwright-test-with-artifacts
spec:
content:
git:
uri: https://github.com/kubeshop/testkube
paths:
- test/playwright/playwright-project
container:
image: mcr.microsoft.com/playwright:v1.32.3-focal
workingDir: /data/repo/test/playwright/playwright-project
steps:
- name: Install dependencies
shell: 'npm ci'
- name: Run tests
parallel:
count: 2
transfer:
- from: /data/repo
container:
env:
- name: PLAYWRIGHT_HTML_REPORT
value: /data/out/playwright-report
shell: 'npx playwright test --output /data/out --shard {{ index + 1 }}/{{ count }}'
artifacts:
workingDir: /data/out
paths:
- '**/*'
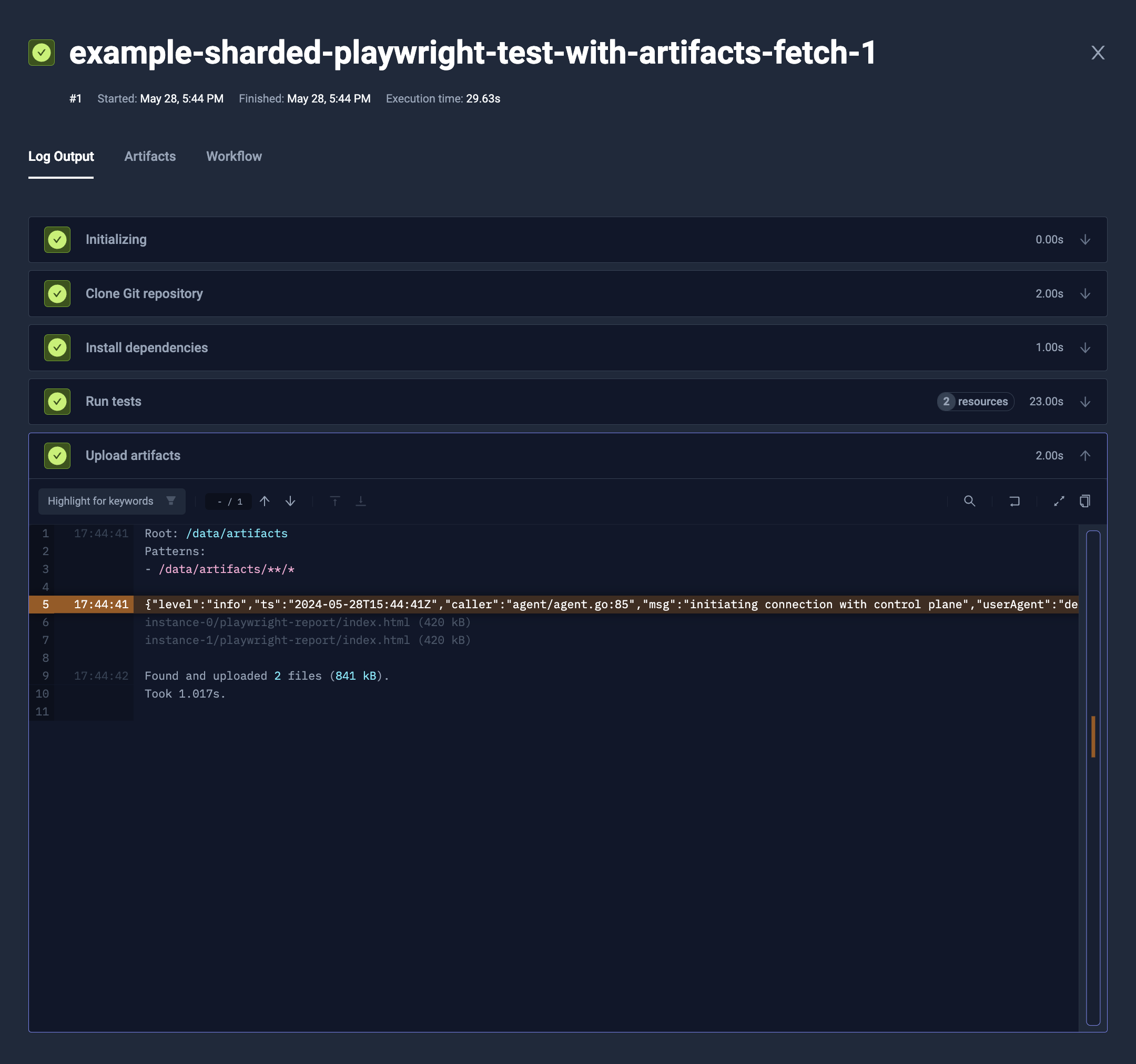
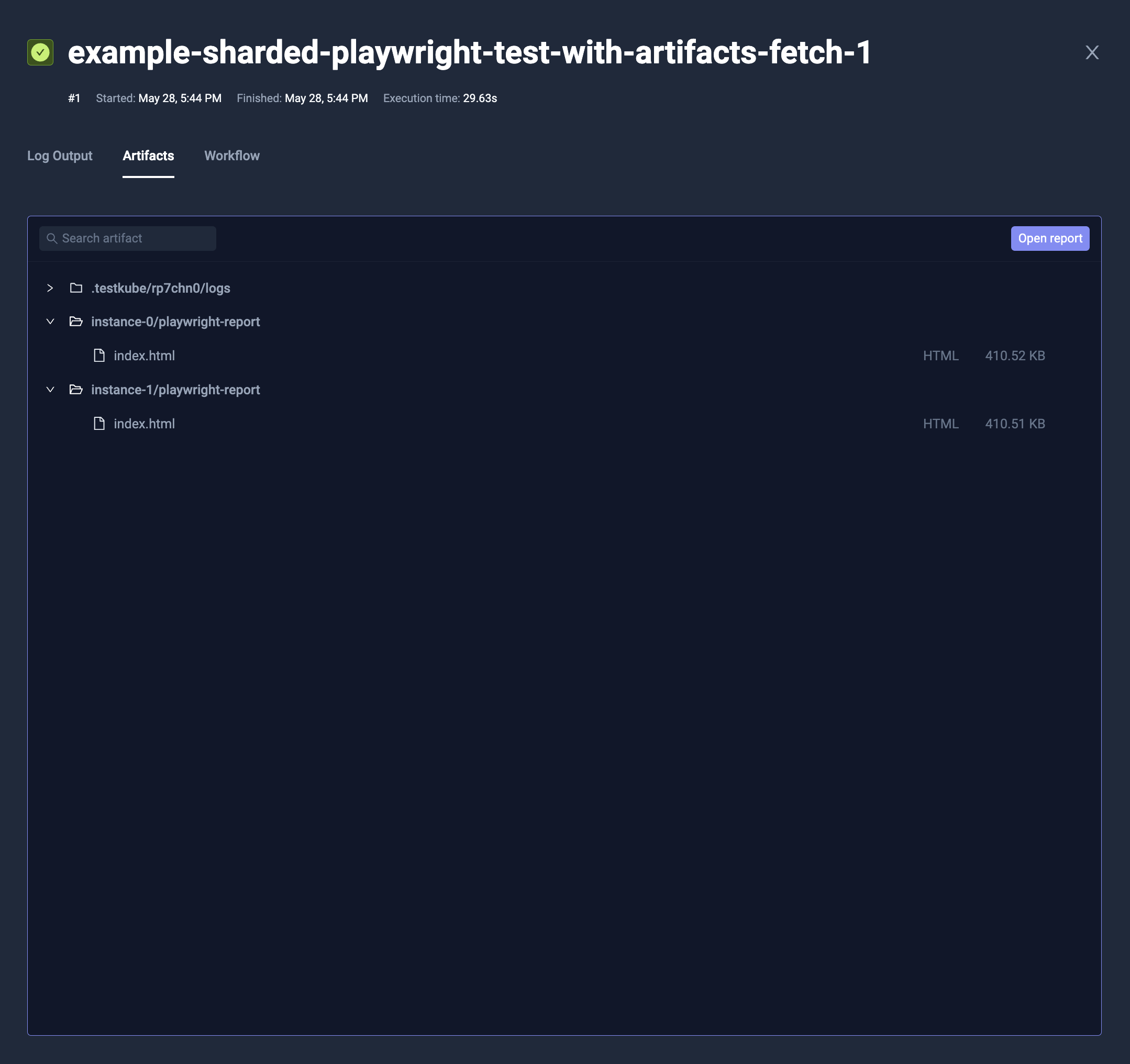
Fetching files back to execution's Pod
Alternatively, you can use fetch instruction. fetch syntax is similar to transfer, but instead of copying data from execution's Pod into parallel instance's Pod,
it's copying the other way - from parallel instance's Pod back to execution's.
Afterward, you can process these files, or i.e. build not isolated artifacts.
- YAML
- Log Output
- Artifacts
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: example-sharded-playwright-test-with-artifacts-fetch
spec:
content:
git:
uri: https://github.com/kubeshop/testkube
paths:
- test/playwright/playwright-project
container:
image: mcr.microsoft.com/playwright:v1.32.3-focal
workingDir: /data/repo/test/playwright/playwright-project
steps:
- name: Install dependencies
shell: 'npm ci'
- name: Run tests
parallel:
count: 2
transfer:
- from: /data/repo
fetch:
- from: /data/out
to: /data/artifacts/instance-{{ index }}
container:
env:
- name: PLAYWRIGHT_HTML_REPORT
value: /data/out/playwright-report
shell: 'npx playwright test --output /data/out --shard {{ index + 1 }}/{{ count }}'
- condition: always
artifacts:
workingDir: /data/artifacts
paths:
- '**/*'
Pod and Job configuration
Each of the parallel workers have own Job and Pod created.
To configure them, use job and pod properties, similarly to the Test Workflow's Job and Pod configuration.
Examples
Sharded Playwright with single report
Blob reporter and merging reports have landed in Playwright 1.37.0, so it's not available before.
Playwright provides nice toolset for sharding, which can be used easily with the Test Workflows.
The example below:
- Load the Git repository with Playwright test (
content) - Install the project dependencies (
steps[0].shell) - Run the Playwright tests split to 2 shards (
steps[1].parallel)- Reserve 1 CPU and 1GB RAM for each shard (
steps[1].parallel.container.resources) - Copy the repository and
node_modulesinside (steps[1].parallel.transfer) - Run Playwright test - with
blobreporter, and with specific shard segment (steps[1].parallel.shell) - Fetch the Blob reporter's data to corresponding directory on Execution's pod (
steps[1].parallel.fetch)
- Reserve 1 CPU and 1GB RAM for each shard (
- Merge the reports using Playwright's tooling (
steps[2].shell) - Save the merged report as an artifact (
steps[2].artifacts)
- YAML
- Log Output
- Artifacts
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: example-sharded-playwright-with-merged-report
spec:
content:
git:
uri: https://github.com/kubeshop/testkube
paths:
- test/playwright/playwright-project
container:
image: mcr.microsoft.com/playwright:v1.38.0-focal
workingDir: /data/repo/test/playwright/playwright-project
steps:
- name: Install dependencies
shell: 'npm install --save-dev @playwright/test@1.38.0 && npm ci'
- name: Run tests
parallel:
count: 2
transfer:
- from: /data/repo
fetch:
- from: /data/repo/test/playwright/playwright-project/blob-report
to: /data/reports
container:
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1
memory: 1Gi
shell: |
npx playwright test --reporter blob --shard {{ index + 1 }}/{{ count }}
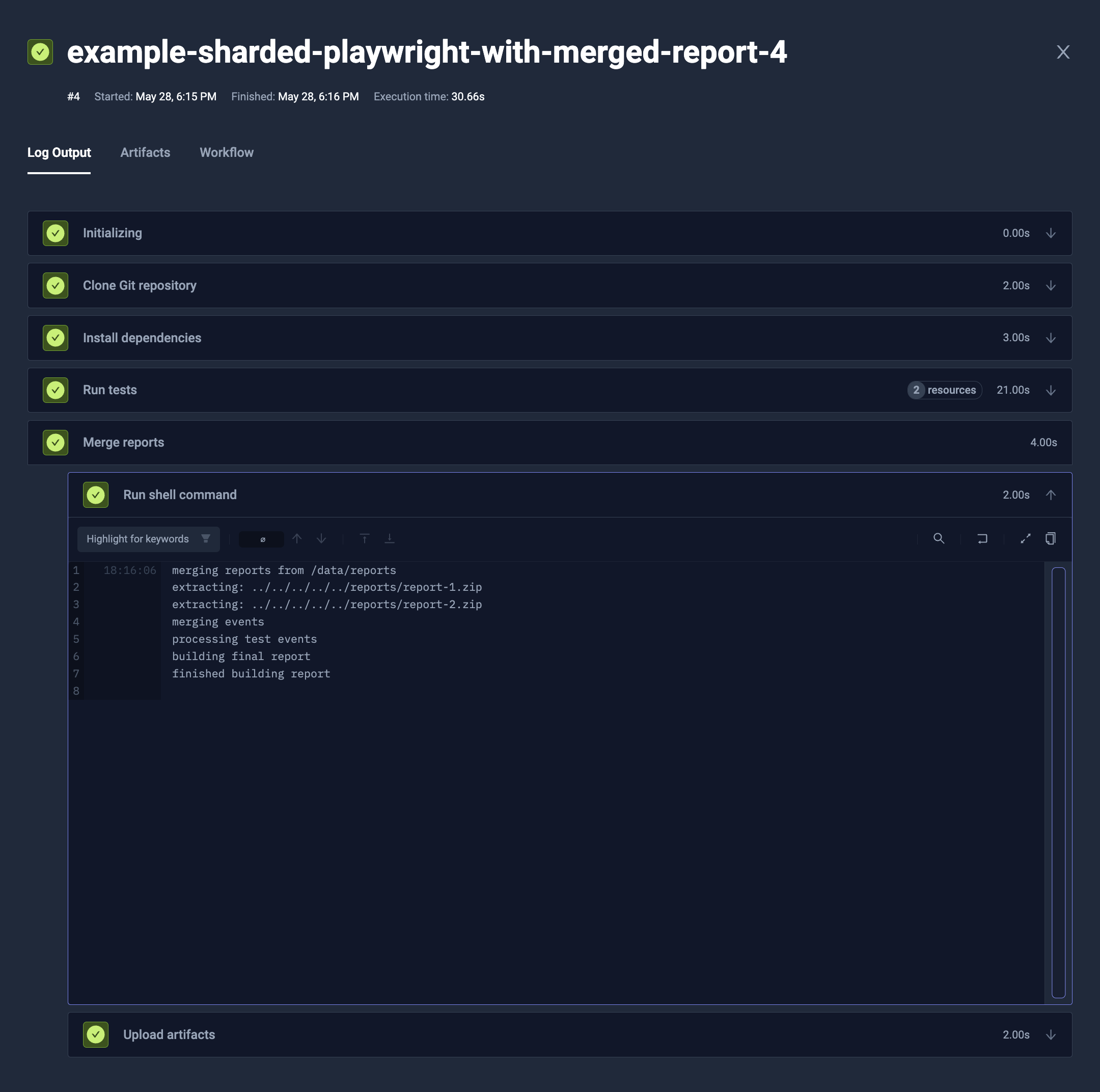
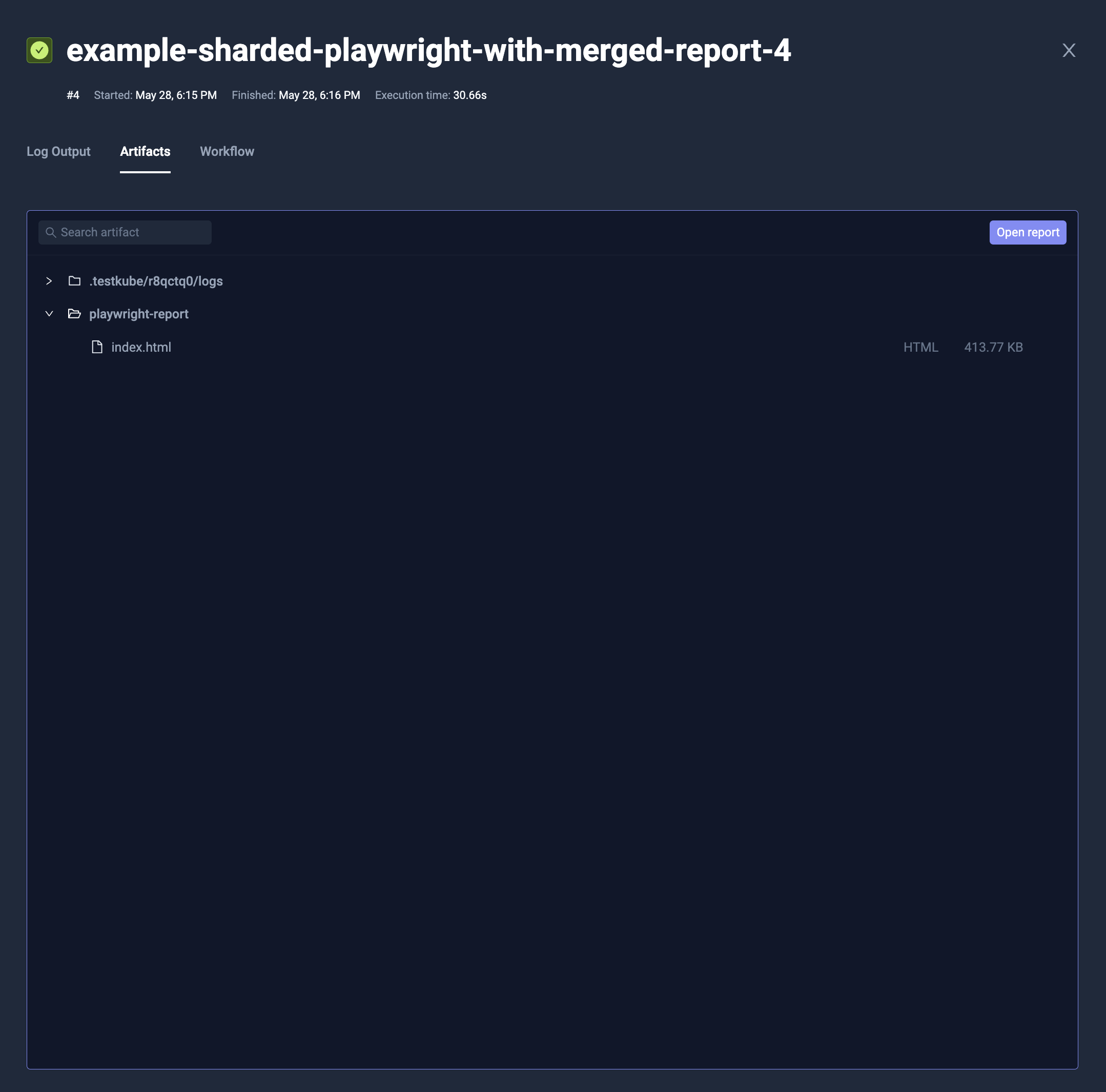
- name: Merge reports
condition: always
shell: 'npx playwright merge-reports --reporter=html /data/reports'
artifacts:
paths:
- 'playwright-report/**'
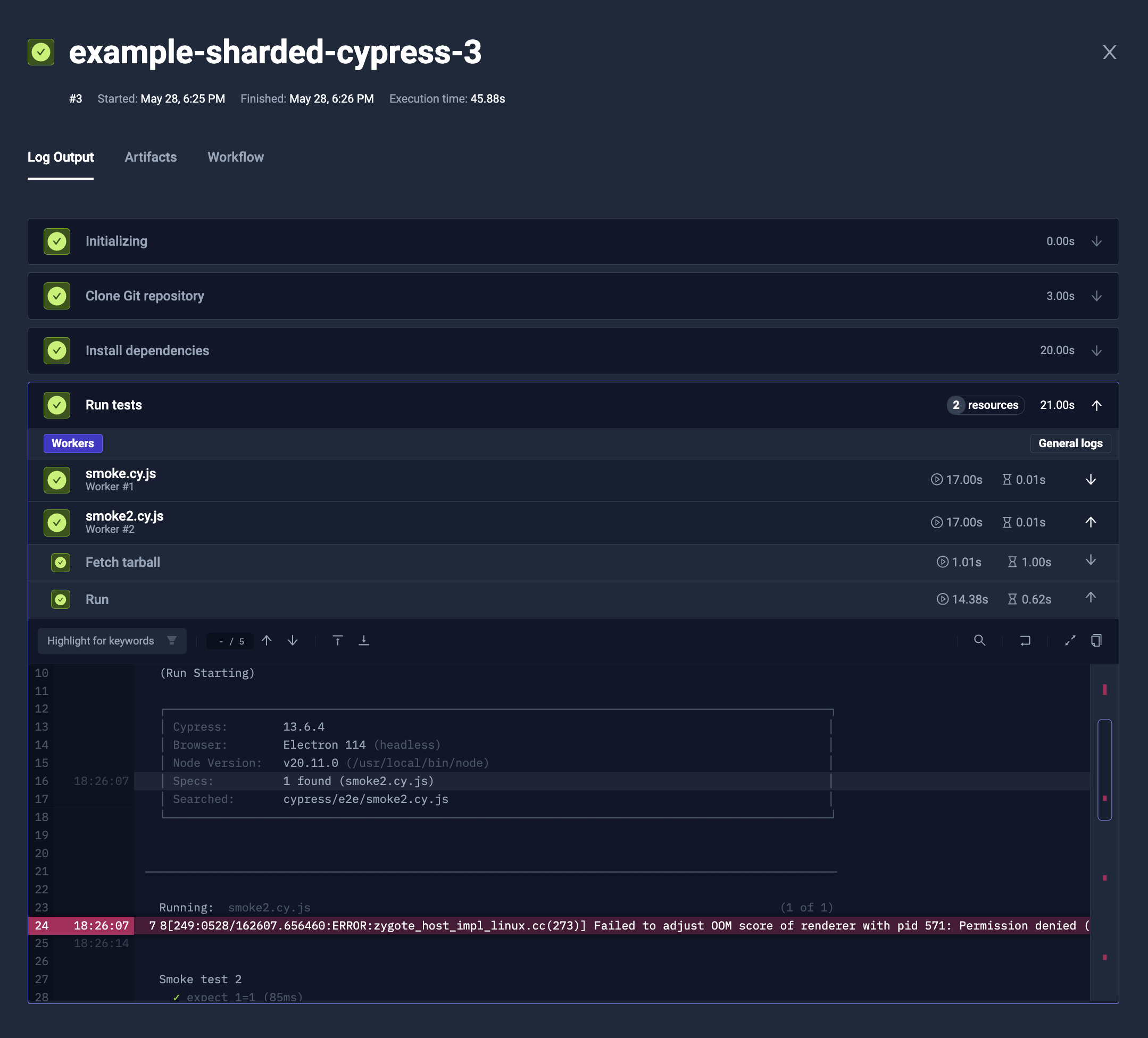
Automatically sharded Cypress tests
Cypress doesn't have any built-in way for sharding, but Test Workflow's matrix and sharding works well with all kinds of tests.
While the example here is not a perfect solution, it's sharding the Cypress tests based on the available test files.
The example below:
- Load the Cypress tests from the Git repository (
content) - Sets the working directory to the tests one (
container.workingDir) - Install the project dependencies (
steps[0].shell) - Run Cypress tests with dynamic sharding (
steps[1].parallel)- The shards will be built off the test files in
cypress/e2edirectory (steps[1].parallel.shards.testFiles) - It will have maximum of 5 shards (
steps[1].parallel.maxCount)- When there is less than or equal to 5 test files, it will run 1 shard per test file
- When there will be more than 5 test files, it will distribute them across 5 shards
- Each shard will run only selected test files with
--specCypress' argument (steps[1].parallel.run.args)
- The shards will be built off the test files in
- YAML
- Log Output
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: example-sharded-cypress
spec:
content:
git:
uri: https://github.com/kubeshop/testkube
paths:
- test/cypress/cypress-13
container:
image: cypress/included:13.6.4
workingDir: /data/repo/test/cypress/cypress-13
steps:
- name: Install dependencies
shell: 'npm ci'
- name: Run tests
parallel:
maxCount: 5
shards:
testFiles: 'glob("cypress/e2e/**/*.js")'
description: '{{ join(map(shard.testFiles, "relpath(_.value, \"cypress/e2e\")"), ", ") }}'
transfer:
- from: /data/repo
container:
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1
memory: 1Gi
env:
- name: CYPRESS_CUSTOM_ENV
value: CYPRESS_CUSTOM_ENV_value
run:
args:
- --env
- NON_CYPRESS_ENV=NON_CYPRESS_ENV_value
- --spec
- '{{ join(shard.testFiles, ",") }}'
Distributed K6 load testing
If you have multiple suites, you may consider exposing such executor as a Test Workflow Template,
and declare contents by config parameters. Alternatively, you can use config directly in Test Workflow.
You can simply run K6 load tests distributed across all your nodes. The mechanism is similar to what k6-operator has under the hood, but it's much more powerful and flexible.
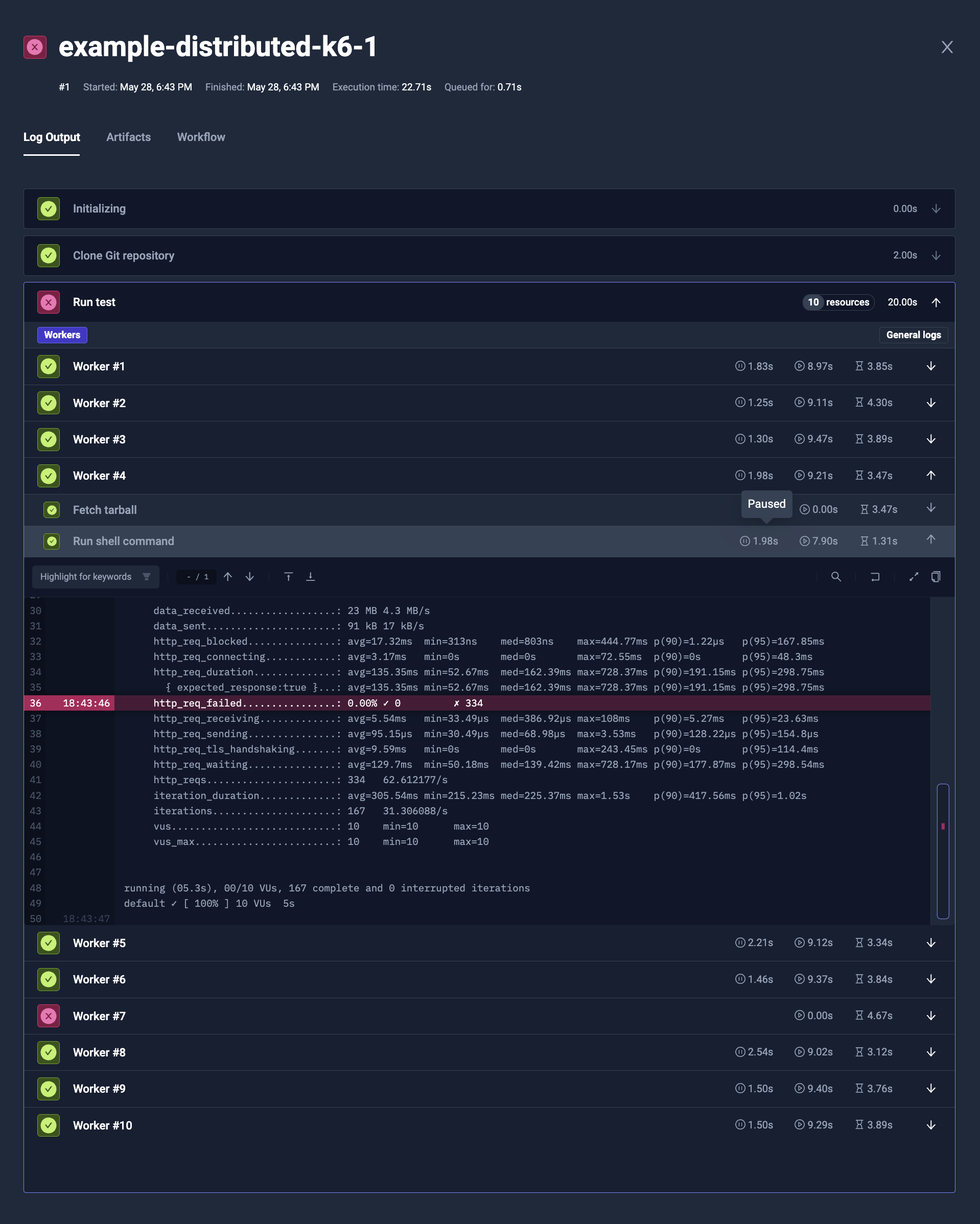
The example below:
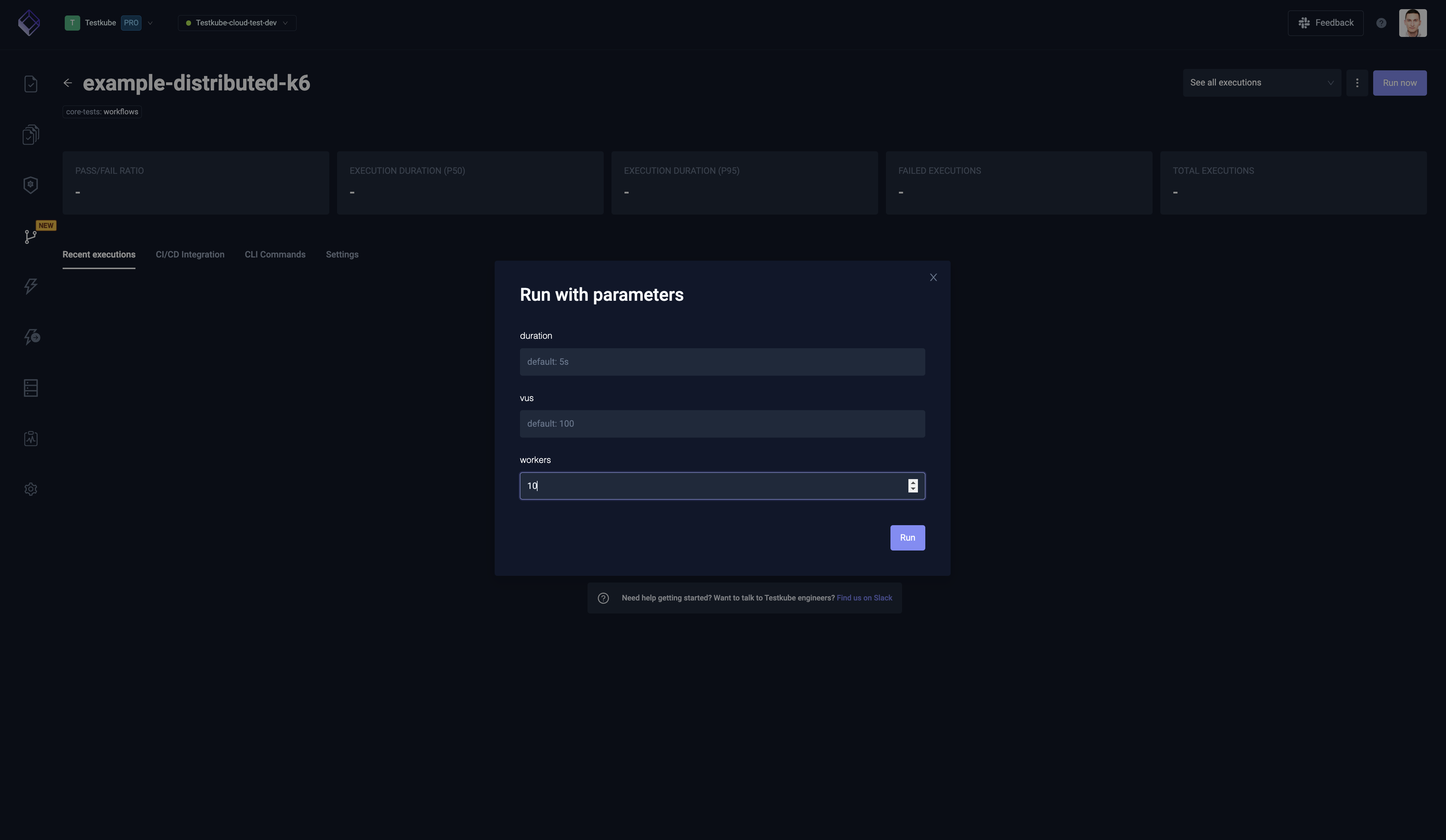
- Takes optional run configuration parameters (
config)vusto declare Virtual Users to distributedurationto declare Load Test timeworkersto declare number of K6 instances to create
- Load the K6 script from Git repository (
content) - Run distributed K6 tests (
steps[0].parallel)- It's using built-in
distribute/evenlyTest Workflow Template, that setspod.topologySpreadConstraintsto distribute pods evenly across nodes (steps[0].parallel.use) - It's creating as many K6 workers as has been declared in
workersconfig (steps[0].parallel.count) - It copies the test case from Git repository into workers (
steps[0].parallel.transfer) - It reserves 1/8 CPU and 128MB for each worker (
steps[0].parallel.container.resources) - It ensures that all workers will start load tests at the same time, when all are ready (
steps[0].parallel.paused) - It runs K6 executable against that test case (
steps[0].parallel.run.shell)- It passes number of Virtual Users and test duration via K6 parameters
- It uses K6 --execution-segment argument to select the fraction of tests to run
- It's using built-in
- YAML
- Run Options
- Log Output
apiVersion: testworkflows.testkube.io/v1
kind: TestWorkflow
metadata:
name: example-distributed-k6
labels:
core-tests: workflows
spec:
config:
vus: {type: integer, default: 100}
duration: {type: string, default: '5s'}
workers: {type: integer, default: 10}
content:
git:
uri: https://github.com/kubeshop/testkube
paths:
- test/k6/k6-smoke-test.js
steps:
- name: Run test
parallel:
count: 'config.workers'
transfer:
- from: /data/repo
use:
- name: distribute/evenly
container:
workingDir: /data/repo/test/k6
resources:
requests:
cpu: 128m
memory: 128Mi
env:
- name: K6_SYSTEM_ENV
value: K6_SYSTEM_ENV_value
paused: true
run:
image: grafana/k6:0.49.0
shell: |
k6 run k6-smoke-test.js \
-e K6_ENV_FROM_PARAM=K6_ENV_FROM_PARAM_value \
--vus {{ config.vus }} \
--duration {{ shellquote(config.duration) }} \
--execution-segment {{ index }}/{{ count }}:{{ index + 1 }}/{{ count }}