Integrating Testkube with Argo Events
Tools like Argo Events help capture Kubernetes resource lifecycle events, such as CREATE, UPDATE, or DELETE. It is capable of detecting and responding to a wide range of cluster events. These events can then be integrated into cloud-native test orchestration platforms like Testkube, allowing teams to automatically run tests that validate the impact of changes, ensuring faster feedback and safer deployments.
This document describes how you can use Testkube with Argo Events. As a prerequisite, you should have good understanding of Testkube, Argo Events and GitOps principles.
For a high-level introduction to using Testkube with Argo Events including a step-by-step tutorial, please check out our integration blogpost.
Prerequisites
- A Kubernetes cluster with Testkube Installed.
- A Kubernetes cluster with Argo Events installed.
- Testkube API Token generated and stored as a
secretinargo-eventsnamespace. - A Test Workflow created and execution webhook generated.
Here is an example GitHub repository with all required configuration manifests.
Execute Testkube Test Workflow with Argo Events
For Argo Events to trigger test execution using Test Workflow, make sure Argo Events is running on a cluster with EventBus configured.
1. Create a Service Account with RBAC
This SA with RBAC will authorize the Argo Events Sensors to monitor ConfigMap in default namespace. Update the rules.resources in Role with resources that you want to authorize access by Argo Events.
# argo-events-sa.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: argo-events-sa
namespace: argo-events
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: argo-events-role
namespace: default
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: argo-events-rb
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: argo-events-sa
namespace: argo-events
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: argo-events-role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
2. Create a resource to monitor for events
This will create a ConfigMap named demo-config in default namespace. Set a set label like watch: "true"
for Argo Events to filter it on event occurrence.
# sample-configmap.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: demo-config
namespace: default
labels:
watch: "true"
component: "testkube"
data:
key: initial-value-1
3. Create a Test Workflow in Testkube Dashboard
Based on the test you want to run, configure a Test Workflow in the Testkube Dashboard using the examples provided by Testkube. Here is a Test Workflow `configmap-k6` that will execute a k6 test and store the artifacts. You can perform test using any testing tool supported by Testkube or Bring your own Test(BYOT).
4. Create an EventSource
Configure an EventSource that will watch the resources like a ConfigMap for ADD, UPDATE, and DELETE events and filter them if they have required label set.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: EventSource
metadata:
name: configmap-eventsource
namespace: argo-events
spec:
template:
serviceAccountName: argo-events-sa
container:
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "128Mi"
limits:
cpu: "500m"
memory: "512Mi"
eventBusName: default
resource:
demo-configmap:
namespace: default
group: ""
version: v1
resource: configmaps
eventTypes:
- ADD
- UPDATE
- DELETE
filter:
labels:
- key: watch
value: "true"
5. Create a Sensor
Configure a Sensor that:
-
Connects to the EventSource resource and provides details of the Kubernetes resource under watch.
-
Sets Testkube Test Workflow execution webhook as http trigger with headers containing Testkube API Token as
secret. -
Adds a label to the Test Workflow with the name of the resources for which the event is triggered.
You can customize the Sensor configuration based on your use case.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Sensor
metadata:
name: configmap-webhook-sensor
namespace: argo-events
spec:
template:
serviceAccountName: argo-events-sa
container:
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
memory: "128Mi"
limits:
cpu: "500m"
memory: "512Mi"
eventBusName: default
dependencies:
- name: configmap-dep
eventSourceName: configmap-eventsource
eventName: demo-configmap
filters:
data:
- path: body.metadata.labels.watch
type: string
value:
- "true"
triggers:
- template:
name: testkube-webhook-trigger
conditions: "configmap-dep"
http:
url: https://api.testkube.io/organizations/tkcorg_b8ddc820d498888/environments/tkcenv_94cb6305566666/agent/test-workflows/<Test_Workflow_Name>/executions
payload:
- src:
dependencyName: configmap-dep
dataKey: body.metadata.name
dest: tags.ArgoEventConfigMapUpdate
method: POST
headers:
Content-Type: application/json
secureHeaders:
- name: Authorization
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: <testkube-auth-secret>
key: <TESTKUBE_API_TOKEN>
retryStrategy:
steps: 3
duration: 10s
backoff:
duration: 6s
factor: 2
jitter: 0.1
6. Verify
a. Verify using the following command that the EventSource and Sensor are running:
$ kubectl get eventsource,sensor -n argo-events
NAME AGE
eventsource.argoproj.io/configmap-eventsource 50m
NAME AGE
sensor.argoproj.io/configmap-webhook-sensor 10m
b. Update the ConfigMap to trigger the execution of the TestWorkflow.
$ kubectl patch configmap demo-config -n default --type merge -p '{"data":{"dummyKey":"test-'"$(date +%s)"'"}}'
configmap/demo-config patched
c. View Sensor logs to verify that Testkube Test Workflow is triggered.
$ kubectl logs -n argo-events -l sensor-name=configmap-webhook-sensor --tail=2
{"level":"info","ts":"2025-06-18T11:25:41.968855251Z","logger":"argo-events.sensor","caller":"http/http.go:193","msg":"Making a http request...","sensorName":"configmap-webhook-sensor","triggerName":"testkube-webhook-trigger","triggerType":"HTTP","url":"https://api.testkube.io/organizations/tkcorg_b8ddc820d498888/environments/tkcenv_94cb6305566666/agent/test-workflows/configmap-k6/executions"}
{"level":"info","ts":"2025-06-18T11:25:43.512504542Z","logger":"argo-events.sensor","caller":"sensors/listener.go:449","msg":"Successfully processed trigger 'testkube-webhook-trigger'","sensorName":"configmap-webhook-sensor","triggerName":"testkube-webhook-trigger","triggerType":"HTTP","triggeredBy":["configmap-dep"],"triggeredByEvents":["e09792772c454a038a7b02efeadc86b2"]}
d. View Test Workflow execution details using Testkube CLI or Testkube Dashboard. Use the following command.
testkube get testworkflow <Test_Workflow_Name>
$ testkube get testworkflow configmap-k6
Context: cloud (2.1.152) Namespace: testkube Org: xxxxxxxx-personal-org Env: xxxxxxx-personal-env
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Test Workflow:
Name: configmap-k6
Namespace: testkube
Created: 2025-06-18 11:03:24 +0000 UTC
Labels: docs=example
Test Workflow Execution:
Name: configmap-k6
Execution ID: 6852a23726359da589bcb641
Execution name: configmap-k6-2
Execution namespace:
Execution number: 2
Requested at: 2025-06-18 11:25:43.041 +0000 UTC
Disabled webhooks: false
Tags: ArgoEventConfigMapUpdate=demo-config
Running context:
Interface:
Type: api
Actor:
Name: noreply@testkube.io
Email: noreply@testkube.io
Type: user
Status: passed
Queued at: 2025-06-18 11:25:44 +0000 UTC
Started at: 2025-06-18 11:25:44 +0000 UTC
Finished at: 2025-06-18 11:25:53.537 +0000 UTC
Duration: 10.496s
The above output shows the Tags added by Argo Event, status and duration of test execution.
Check Testkube Dashboard for deeper insights like execution logs, artifacts and resource utilisation during test execution.
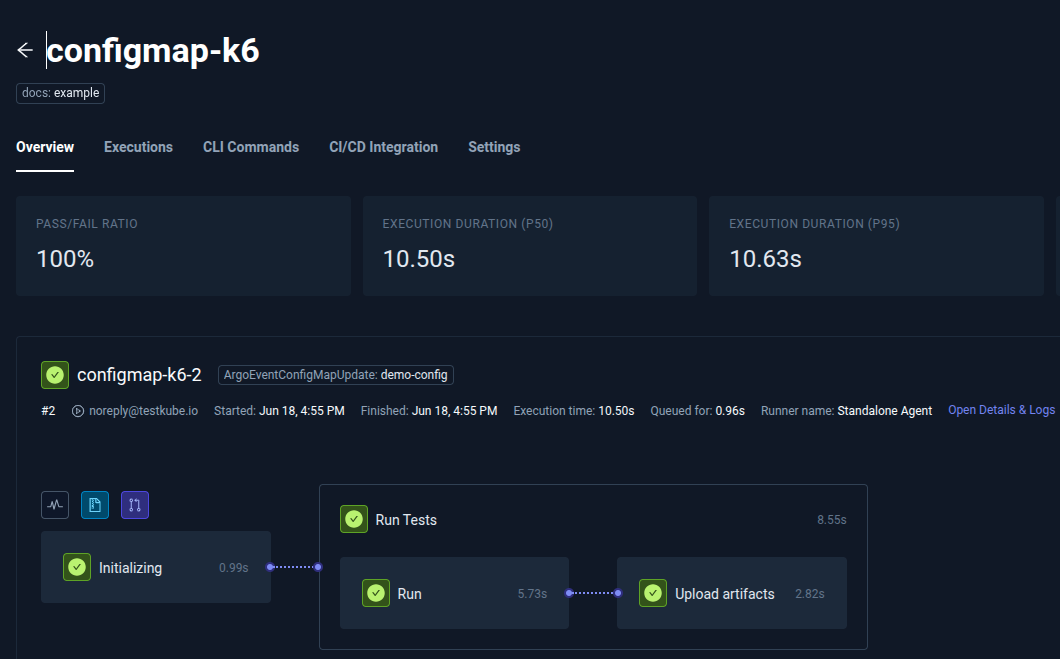
The execution of the Test Workflow is triggered and completed successfully.
The tags configured in the Sensor configuration helps verify that the request is coming from ArgoEvent.
Check the Executions in Testkube Dashboard to see if the tag is added.
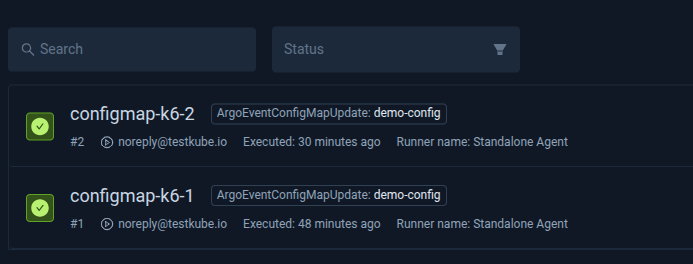
Tag ArgoEventConfigMapUpdate is added to the execution along with the name of the ConfigMap demo-config.
Select Test Workflows execution and view the Log Output.
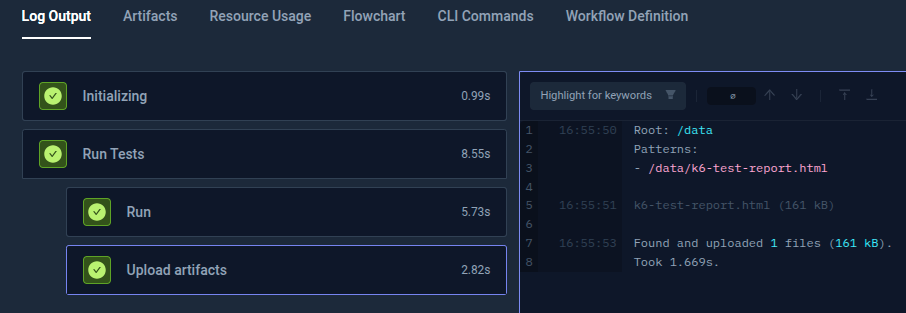
Select the Artifacts and view the test results.
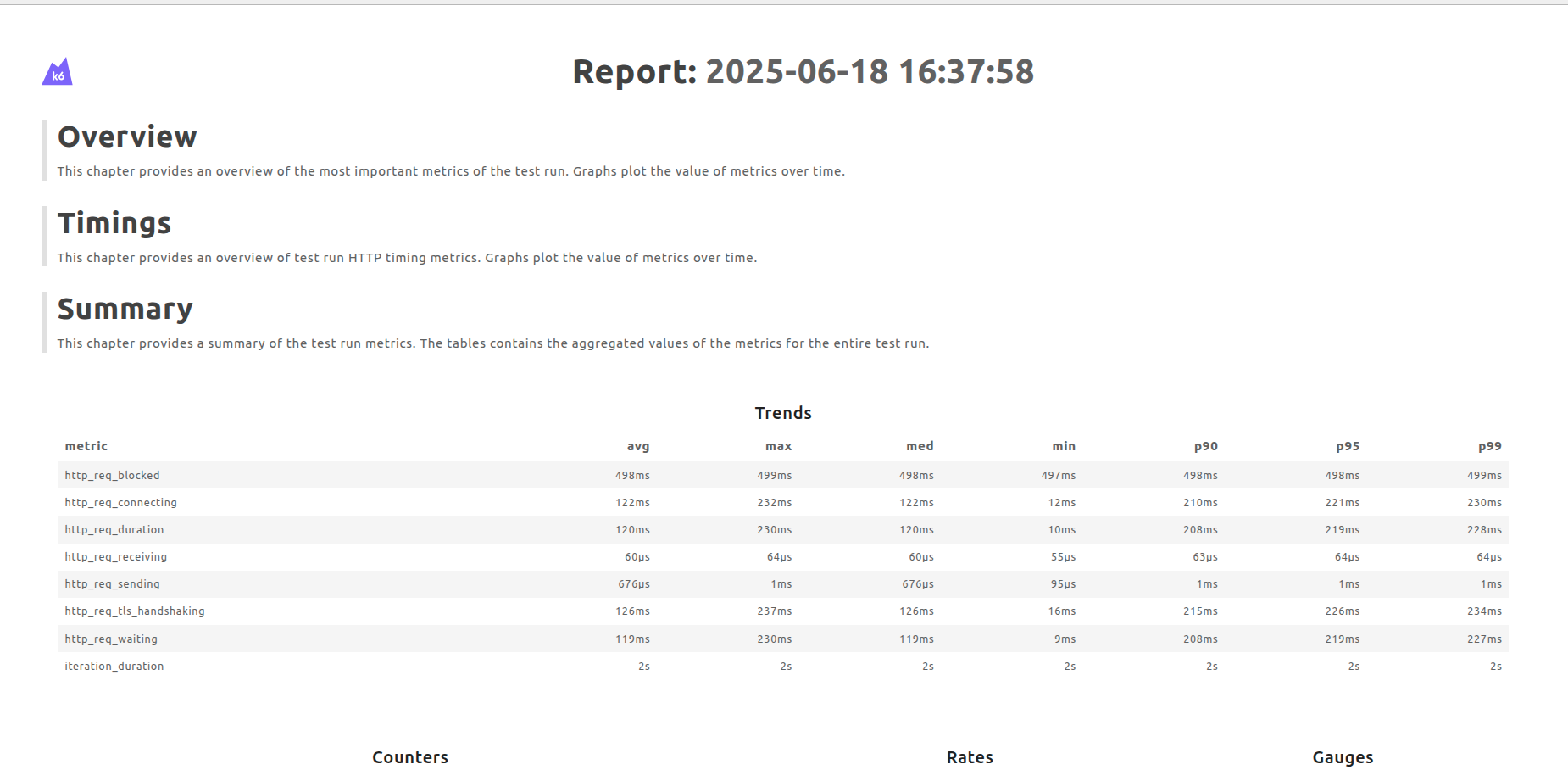
Monitor Resource Usage including CPU, memory, network traffic and disk usage across each test execution.
This setup enables a reliable, event-driven testing workflow in Kubernetes by integrating Argo Events with Testkube. It ensures that any resource change automatically triggers targeted tests, helping teams validate changes early and maintain application stability.