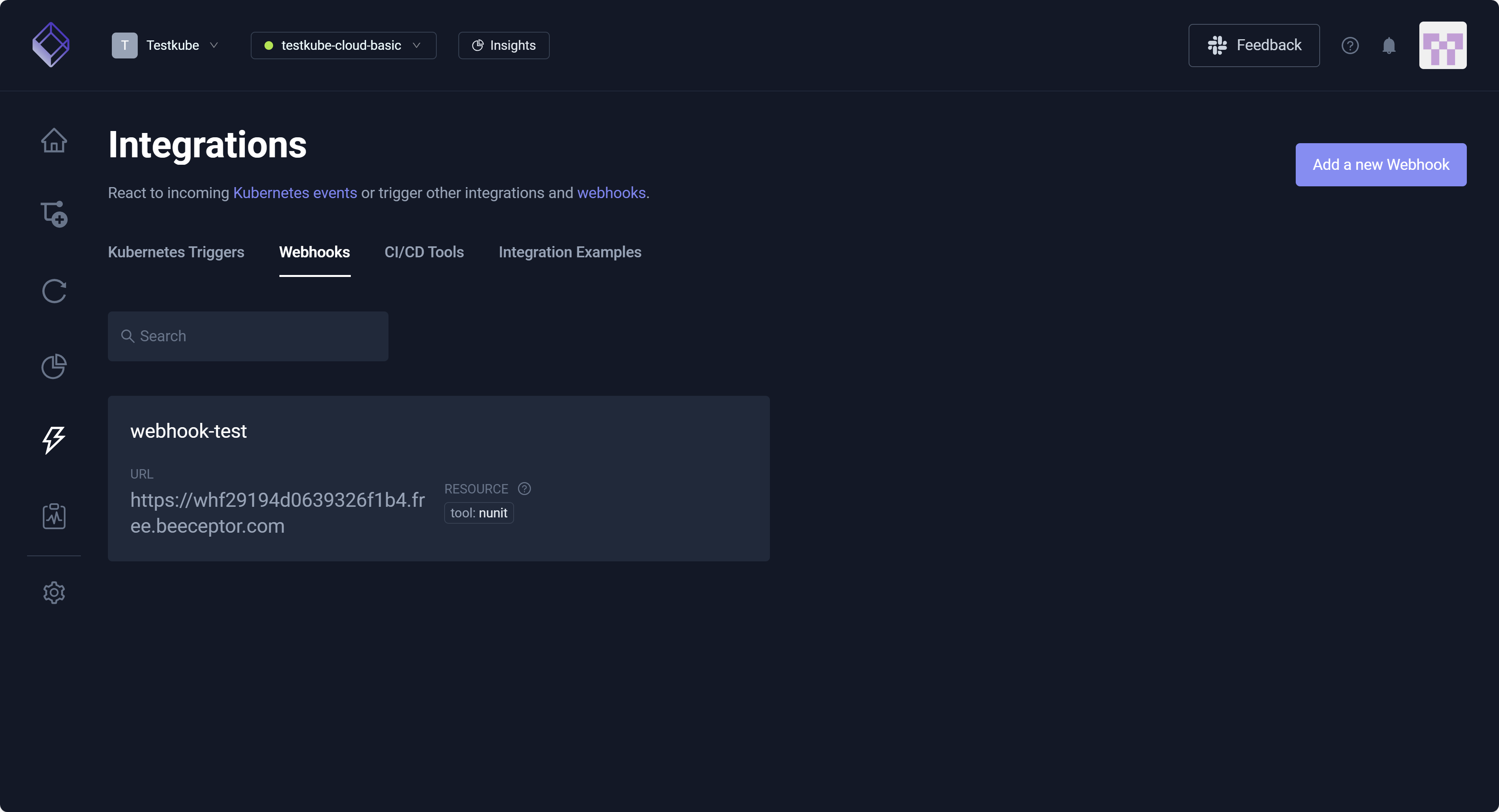
Integrations Webhooks
Webhooks are event-driven and invoke HTTP endpoints exposed by external systems, such as CI/CD tools, GitHub, Slack, or other services. You might create a Webhook, for example, to notify your team if a critical API test fails so the team can fix the issue immediately. If this test finishes with a Failed status, Testkube (based on your Webhook configuration) sends an HTTP POST request to a Slack Webhook URL which then posts a message in the Alerts channel. The Slack Webhook URL is a private entrance (of sorts) to the Alerts channel, automatically turning data into a chat message for your team. This allows Testkube to communicate with Slack without the need for you to manually copy/paste this message.
You can create and manage Webhooks in your Environment via the Testkube Dashboard, selecting Integrations from the left navigation pane then proceeding to the Webhooks tab. For additional information, read Webhooks.
Creating a New Webhook
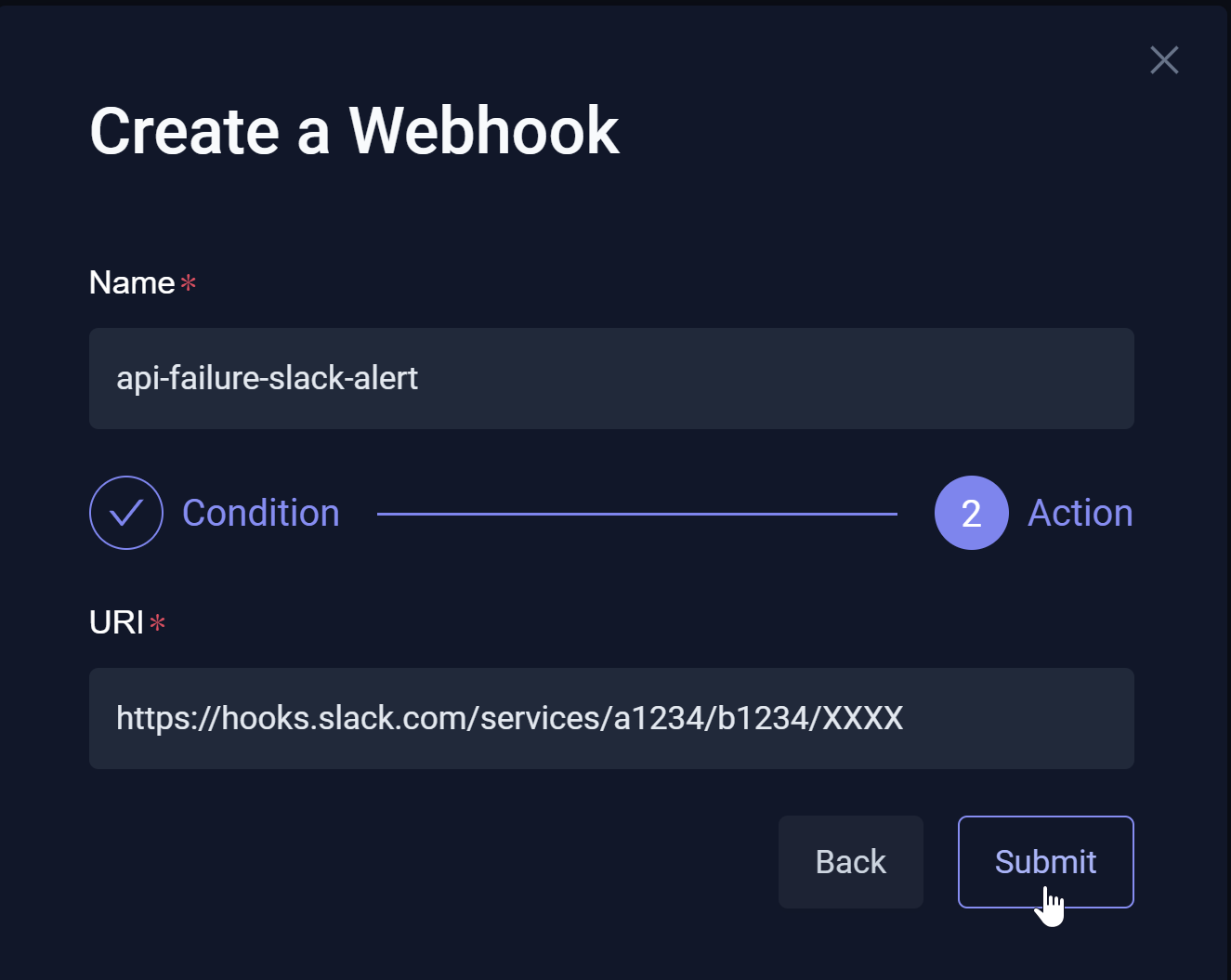
You can select Add a new Webhook to access the Create a Webhook modal.
Webhook Condition
The Create a Webhook modal displays:
- Name – Unique identifier that must represent a valid Kubernetes name, as Webhooks are stored as Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) in your cluster.
- Resource Identifier – The who watched, such as a specific test. Resources follow the official Kubernetes selector pattern. Multiple selectors are grouped by the AND operator.
- Triggered events – The what or specific Kubernetes action that causes the Testkube Webhook to run, such as a Failed test status.
EXAMPLE
When a Testkube test finishes with a Failed status, Testkube sends an HTTP POST request to a Slack Webhook URL which then posts a message in your Alerts Slack channel to notify team members. For additional information, read Slack Integration.
- Enter the Name, Resource identifier, and Triggered events.
- Select Next.
- Name auto-populates from the Name field on previous screen.
- Enter the URI or digital mailing address of the external app where Testkube should send the update, such as a Slack channel.
- Select Submit.

Webhook Settings
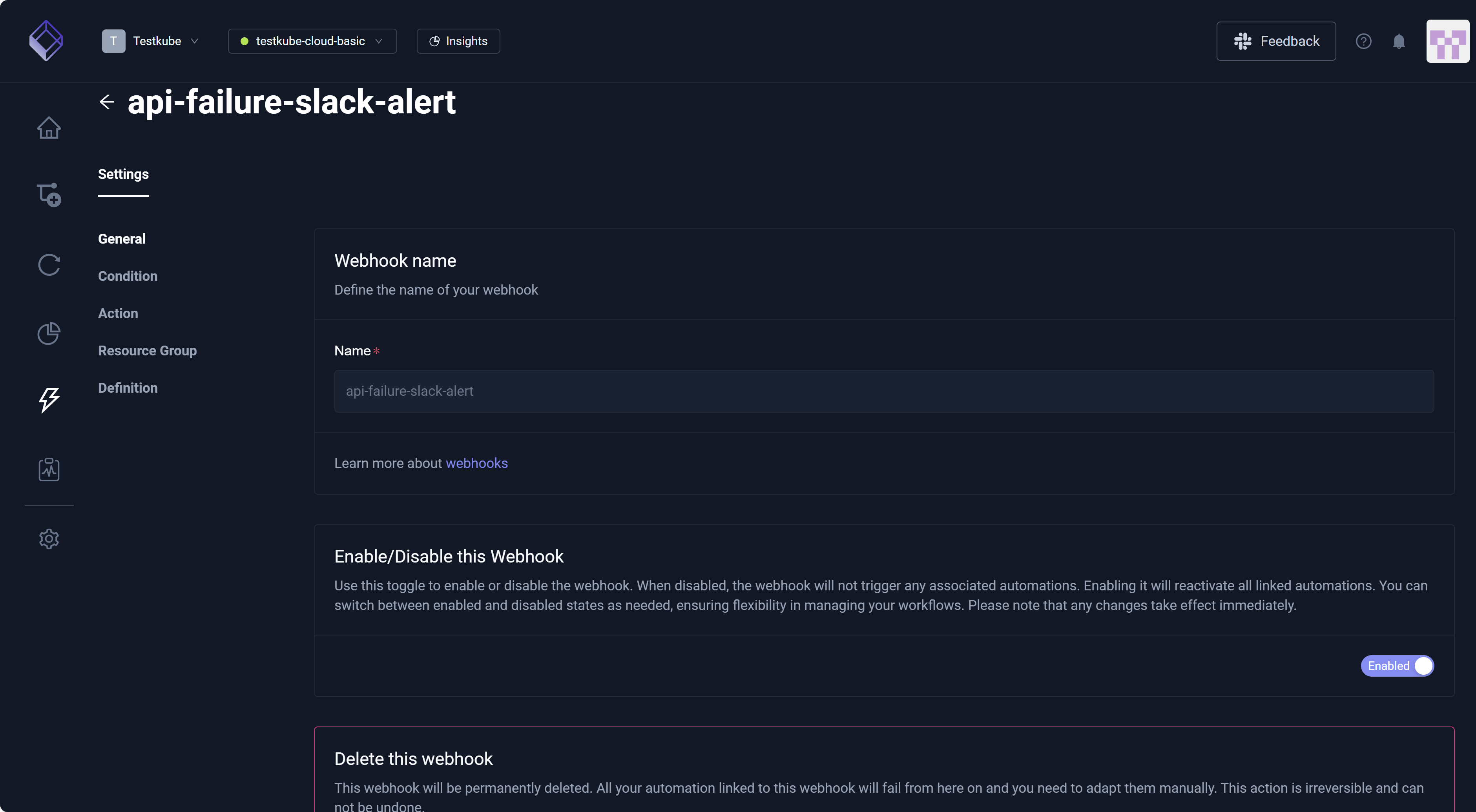
You can select an existing Webhook to view its Settings, which provides access to General, Condition, Action, Resource Group, and Definition.
Settings exposes basic configurations. For additional information, read Resource Selector and Webhook Payload. You can modify the generated YAML directly in the Definition associated with the Webhook you selected.
General
The General setting allows you to access Name, Enable/Disable this Webhook, and Delete this webhook.
You can disable a Webhook for specific Workflow Executions. For additional information, read Disabling Webhooks.
Condition
You must define the Condition that must be satisfied such that there are calls to this Webhook. This setting includes Webhook condition, Resource identifier, and Triggered events.

Action & Payload
Action defines the target URI associated with this Webhook. The Custom Payload field allows you to customize the payload you will send with each request. In the context of our Example, the payload is the Slack message sent to team members. For additional information, read Webhook-Payload. This setting also displays Headers (customizable and can be sent with each request) and Add a new variable.

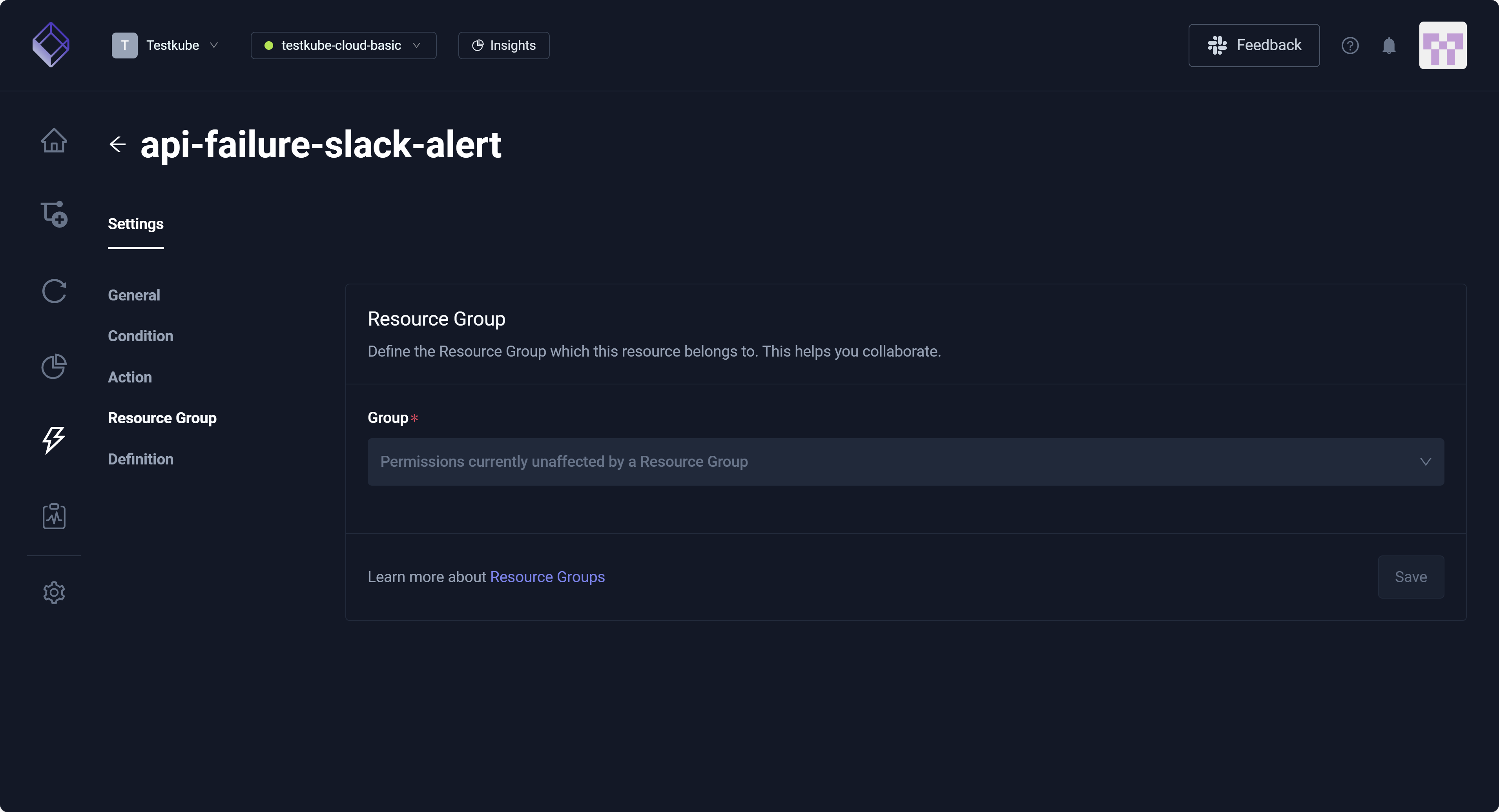
Resource Group
This setting identifies the Resource Group that contains this Webhook. For additional information, read Resource Groups.
Definition
This setting displays the underlying YAML for your Webhook, enabling you to manually configure the Webhook as opposed to navigating each Setting.
If you want to hide the Webhook YAML definition in the Dashboard because it contains sensitive information, you can enable Webhooks URL Masking under Organization Product Features which hides the Definition tab under the Webhook Settings.

Credentials
Webhooks often need to call external systems that require authentication (for example, API tokens or secrets).
Instead of hard coding these sensitive values into your Webhook definition,
Testkube allows you to securely inject them from Credentials using the {{credentials(<NAME>)}} template function.
You can reference Credentials in:
- Webhook URL
- Headers
- Payload template
Example:
apiVersion: executor.testkube.io/v1
kind: Webhook
metadata:
name: example-webhook
spec:
events:
- end-testworkflow-success
uri: https://webhook.example.com/test?token={{credential('TOKEN')}}
headers:
X-API-Token: "{{credential('HEADER_TOKEN'}}"
selector: test-type=k6
payloadTemplate: "This template includes an inline secret: {{credential('SECRET'}}"
Visit our Testkube Credentials docs to learn how to create and manage Credentials used in Webhooks.